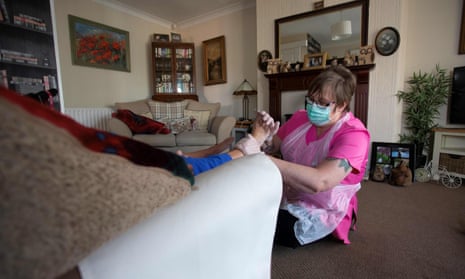
Nearly 9,000 people in England are waiting for home care services according to figures obtained by the Observer, but the true figure is likely to be much higher with the situation having worsened dramatically since last spring.
Home care is provided to elderly or disabled adults in their home to help with essential tasks, such as cooking and personal care.
According to Freedom of Information responses from 96 councils in England, 8,808 people have “unallocated” or unsourced hours of home care, meaning they are not getting the home care they have been assessed as needing. The overall number of unsourced hours rose from 15,905 in April 2021 to 60,664 in December.
People with unsourced care may be going without, but are more likely to be receiving care in a less appropriate setting, such as in hospitals or care homes, or being looked after unpaid by family members.
Caroline Abrahams, Age UK’s charity director, said: “It comes to something when so many paid-for hours of care are not being used, all because there aren’t enough staff to put them into effect. This inevitably means that growing numbers of older and disabled people are going without the care and support they need, and that where unpaid carers are helping their loved ones, they are being forced to do more for longer, unaided and with no chance of a break.
“The prospects for anyone who is waiting for care and on their own, without family or other support, are extremely grim – one has to wonder how some of these people are managing to carry on at all.
“It is tempting for policymakers to place all the blame for the growing care workforce crisis on Covid-19 … but it’s been coming for a long time. Where we are now is what happens when there is no effective workforce planning over many years. It would be hard to exaggerate how worried we are about what’s going to happen to home care this year, and to the millions of older and disabled people who rely on it every day.”

Jane Townson, chief executive of the Homecare Association, said retention and recruitment of care workers is “more difficult than ever”, blaming “inadequate government investment in social care”. Many staff, she said, leave for better paid jobs in sectors such as retail and hospitality.
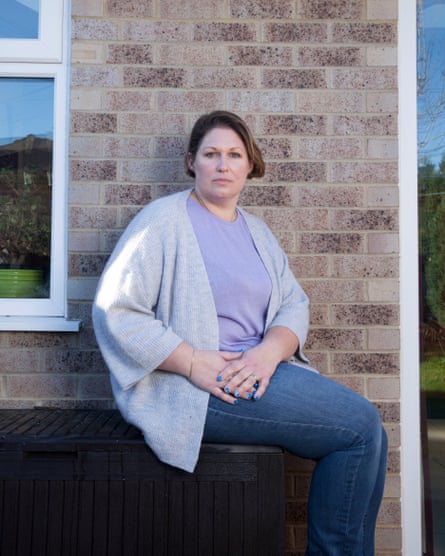
“We are struggling massively to have any support whatsoever,” Ellen Fenby, whose 19-year-old son is severely disabled, told the Observer. “There’s a lack of staff, there’s a lack of people in the industry, there’s a lack of being able to train people to come in and support us. Since July of last year we have had no support in the home whatsoever.”
Fenby’s son has multiple medical needs including brain damage and internal organ problems. Last summer he had to have a PEG tube fitted, which allows feeding directly into the stomach, after he developed severe problems swallowing.
“He went from a young person eating normally like everybody else does, to all of a sudden not being able to eat by his mouth, everything by his PEG. We were having to do that feeding, we were having to manage the care of the stoma site, the care of his food and making sure his nutrition and hydration was correct. So his care need grew significantly.”
Their local council assessed he needed more care – two hours of home care every eveningfor personal care and his feeding regime. The council increased the funding for Fenby’s son but the family can’t spend it as no provision is available. “It’s sitting there. We’ve been paid the money from the council, and we simply cannot find anybody to be able to actually take those hours,” said Fenby.
“It has been very stressful. Both my husband and I have full-time jobs, we have three other children. Trying to make sure he still has his care needs met while trying to seek other agencies – I’m constantly emailing all the agencies in the area to try and see if there is anybody. There is a massive lack of anybody that is PEG-trained.”
Nor can they spend the money on other forms of care. Her son’s mental health has suffered, his needs have grown and new elements of his disability have emerged.
“We have come to a point where we are a family in crisis, because the need has grown significantly that we are struggling to cope,” Fenby said.
A Department of Health and Social Care spokesperson said: “We are committed to delivering world-leading social care across the country and that is why we’re investing an additional £5.4bn over three years to reform adult social care.”