- Feb 25
- AddictionMental Health Treatment
Much like our physical health, mental health is an integral aspect of a person’s overall well-being and is essential in determining how we feel, think and act. From daily stressors to significant life events, everyone has things they may worry about in life that trigger feelings of nervousness.
However, experiencing uncontrollable worry and fear about everyday experiences and situations can prove detrimental to your quality of life. If you have constant and debilitating feelings of anxiety and dread that interfere with your work, responsibilities and social life, you may be living with an anxiety disorder that affects more than 6.8 million U.S. adults.
What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is an anxiety disorder in which people experience excessive and persistent feelings of nervousness about many events or activities. GAD differs from the occasional anxiety we recognize within our inherent neurological “fight or flight” response. When we are stressed, our brain produces a hormone known as cortisol, which alerts us to danger and increases the flow of adrenaline through our bodies to heighten our heart rates and blood flow.
While anxiety can help us navigate stressful and dangerous situations by momentarily boosting our energy, too much anxiety that is out of proportion to the actual stimuli can be destructive. GAD may cause you to avoid places and people in your life to prevent periods of intense anxiety and terror that may result.
With GAD, a person’s brain constantly generates intense fear, concern and stress, which do not subside like normal anxiety usually does. As a result, the fearful sensation remains and builds into uncontrollable worry that people cannot put out of their minds. People with GAD may experience an array of common worries regarding future events, past incidents and behaviors, perceived personal shortcomings, personal health and safety risks, family matters and personal abilities.
Symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD develops gradually, but there are several signs associated with the disorder that can indicate its presence. General mental and emotional symptoms of GAD may include:
- Persistent or all-encompassing feelings of worry or anxiety out of proportion to the actual events
- Difficulty controlling feelings of nervousness or apprehension
- Overthinking solutions and plans to all possible worst-case scenarios
- Difficulty dealing with uncertainty
- Perceiving harmless events and situations as threatening
- Difficulty concentrating
- Indecisiveness and constant fear about making the wrong decision
- Feeling tense, restless and unable to relax and set aside worry
GAD may also cause several physical symptoms in both adults and children that can make it difficult to function daily. Some of these symptoms include:
- Fatigue and feeling constantly tired
- Difficulty falling or staying asleep
- Muscle tension, aches or twitches
- Excessive trembling or shaking
- Being easily startled
- Nausea, diarrhea or intestinal issues
- Excessive sweating
- Irritability or feeling “on edge”
- Having a hard time swallowing
- Constant urge to use the bathroom
- Feeling light-headed
- Headaches, stomach aches or other body pains
Symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder are often worse during periods of high stress, such as during school exams, a physical illness or a family or relationship conflict. Adults with GAD may often experience intense anxiety over everyday circumstances such as family health and safety, job security and performance, financial security and performing household chores and responsibilities.
Children with GAD can experience worry about their academic and athletic performances or experience heightened fear regarding world catastrophes and natural disasters such as earthquakes, tornadoes and wildfires.

Causes and Risk Factors of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Psychologists have identified several causes of GAD and risk factors that may increase your chances of diagnosis.
Causes
Much like other anxiety disorders, generalized anxiety disorder can develop from a complex interaction of biological and environmental factors, including:
- Differences in brain chemistry and function
- A genetic tendency toward excessive anxiety
- Perception of environmental threats
- Temperament and ability to cope with stress
Risk Factors
A risk factor is a trait or experience that increases your likelihood of developing a condition or disorder. Some factors that may increase the risk of developing GAD include:
- Biological sex: Women are twice as likely as men to receive an anxiety diagnosis due to differences in hormone fluctuations and brain chemistry.
- Family history: The risk of GAD may be higher if a history of anxiety runs in your family. The presence of chronic medical illnesses or other mental health disorders may also increase your chances of developing GAD.
- Personality: Individuals with certain personality types are more prone to anxiety disorders than others. People who avoid anything dangerous or who have lower self-esteem may be more likely to develop GAD.
- Experiences: People with GAD may have a history of significant life changes or recent stressful, traumatic or negative life events. Recent or prolonged exposure to stressful situations, including personal or family illnesses, can increase your risk, as can living at a lower socioeconomic level.
- Childhood abuse: Adverse and traumatic experiences such as childhood physical and sexual abuse can increase your risk of developing GAD.
- Substance use: Excessive caffeine, tobacco, alcohol and drug use can exacerbate existing anxiety and contribute to GAD.
How Do You Diagnose Generalized Anxiety?
A health care provider or mental health professional will typically diagnose GAD and can determine whether your symptoms are indicative of another health problem, such as an additional mental health condition or substance use disorder. By asking detailed questions about your medical history and any current symptoms, your physician can understand what you are experiencing. As signs of GAD tend to occur every day, symptoms that last at least six months or longer can be a strong indication of the presence of GAD.
A physical exam will help assess possible signs of GAD and indicate whether certain medications or underlying medical conditions exacerbate your anxiety. Your physician may also order blood or urine tests if they suspect that an additional medical condition contributes to your symptoms.
GAD is often co-morbid with panic disorder, depression, schizophrenia and other mental health conditions. A mental health screening and additional psychological questionnaires will help your physician and psychiatrist understand how anxiety affects your life.
By performing a psychological evaluation based on the criteria of GAD listed in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), your physician or a psychiatrist can determine the validity of a GAD diagnosis.
How Do You Treat GAD?
So what can you do to prevent yourself from succumbing to excessive worry? Several treatment options have proven effective in combatting symptoms of GAD and increasing one’s overall quality of life.
Psychotherapy
Speaking with a therapist can help immensely in mitigating symptoms of GAD. One type of psychotherapy called cognitive behavioral therapy is especially useful for treating GAD. It teaches a person different ways of behaving, thinking and reacting to anxiety-inducing situations. Cognitive behavioral therapy involves regularly speaking with a mental health professional with the goal of permanently changing how you approach stressful stimuli and life events.
Cognitive behavioral therapy has also provided numerous individuals with long-term anxiety relief as it allows patients to recognize and control disproportionately anxious thoughts. Your therapist can also work with you to learn reliable self-calming methods when GAD causes upsetting thoughts.

Medication
Several medications also can help treat GAD, and your doctor will most likely create both short-term and long-term medication plans for you regarding treatment. Short-term medications called anti-anxiety medications can help relax one’s body and ease the physical symptoms of anxiety such as muscle tension, fatigue and nausea. Some medications your doctor can prescribe to help treat GAD may include:
- Antidepressants: While people usually take selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) to treat depression, they are also helpful to address symptoms of anxiety and GAD. While they may take several weeks to start working, these medications cause minimal side effects and allow you to increase your dosage slowly over time for increased effectiveness.
- Benzodiazepines: Your doctor may prescribe a benzodiazepine for more immediate relief from anxiety symptoms in limited circumstances. Doctors usually reserve sedatives such as benzodiazepines for relieving acute anxiety on a short-term basis. As benzodiazepines can be habit-forming, these medications are not ideal for those who have struggled with substance use disorders.
Your doctor can work with you to find the best medication and dosage amount for you.
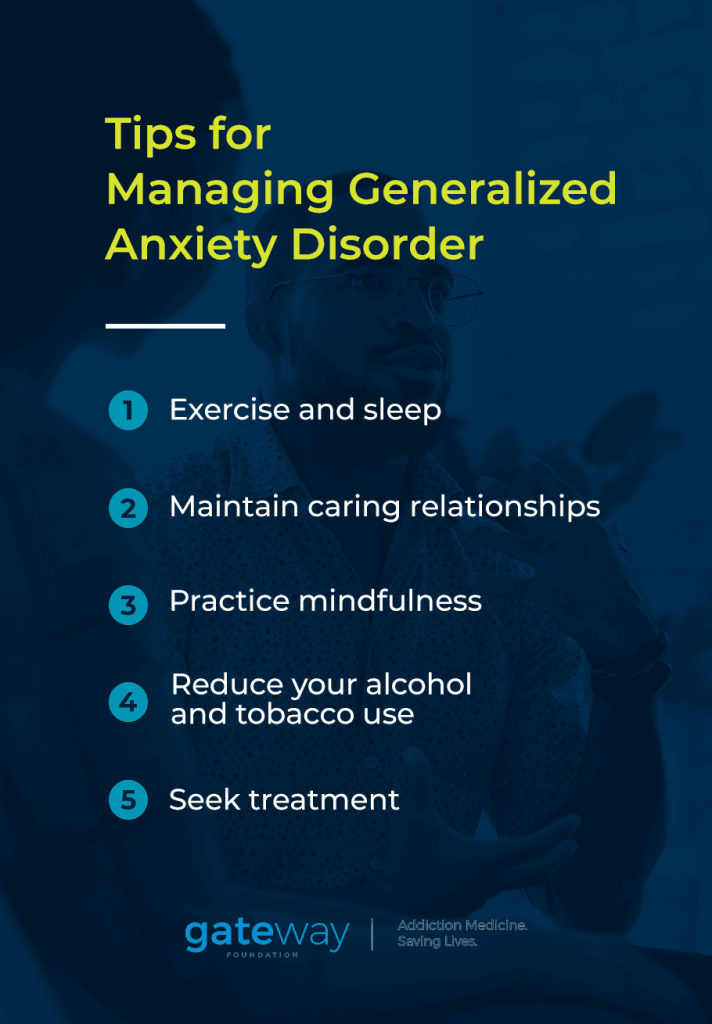
Tips for Managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Many people have found relief from their anxiety by adopting several lifestyle changes to help manage GAD for a better life outlook.
Live a Consciously Healthier Lifestyle
A healthier lifestyle can ultimately help you improve your mental health and reduce the severity of your GAD symptoms. Take action in various areas to live a healthier life:
- Eat healthy: A healthy diet filled with lots of fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean meats such as fish may reduce feelings of intense anxiety. Eating good food is vital to fuel your body, boost your mood and gain sufficient energy to make it through your day.
- Exercise: Exercising regularly will also help lessen your GAD symptoms. As you stay physically active, you will flood your body will calming, happiness-inducing endorphins that are effective at reducing stress. Yoga and meditative practices will also help promote mindfulness and let you self-reflect on feelings of worry, anxiety and other negative emotions. You may find it wise to start slowly and gradually increase the level of intensity of your activities.
- Get enough sleep: It is essential that you get plenty of sleep every day to stay healthy. You can use a variety of relaxation techniques to help you calm down and ease any anxiety before bed to make sure that you get enough sleep to feel rested. Remember to contact your doctor if you are having trouble sleeping or experiencing insomnia.
Increase Your Socialization
Surrounding yourself with people who support you can go a long way toward recovery from GAD and feeling more in control of your fears and emotions. Find ways to continue participating in enjoyable activities and maintain social interaction and caring relationships with loved ones.
Talking with a spouse, a trusted friend or family member about your anxiety and worries can also help you to take control of your GAD. Finding people to rely on through social coping strategies can also help you feel better about yourself and increase your level of self-confidence.
Take Action in Confronting Your Fears
One crucial aspect of managing GAD is learning to cope with persistent anxious thoughts and fears and combating them through mindfulness. By working consistently with a therapist or other treatment provider, you can figure out what triggers your anxiety and focus on improving your reaction to it.
When you can sense yourself becoming anxious about something, you can take a walk or find something enjoyable to refocus your mind and distract you from worrying stimuli. It will also help you to focus on the present moment rather than events in the past, which you lack control over. Practicing and maintaining a positive attitude will also help you redirect attention from your fears and focus more on what you can enjoy in life.
Reduce Your Substance Use
Drinking alcohol, smoking and using recreational drugs can exacerbate and worsen symptoms of GAD. Even caffeine-filled drinks can negatively impact your anxiety level. Avoiding stimulants and drug use will help you gain a handle on controlling your anxiety and managing your emotional reactions to life events and situations.
If you are struggling with addiction, Gateway Foundation can help. At Gateway, we offer a 12-step support group with substance use disorder-focused treatment. Being in an environment centered on compassion, understanding and shared experiences can help you address substance misuse and become more mindful of habits that may worsen the effects and symptoms of mental health conditions.
Seek Treatment From Mental Health Professionals
From counseling to medications, finding and maintaining a treatment plan is a huge step toward seeking help for GAD and addressing debilitating symptoms. But remember that it’s essential to prioritize consistency by sticking to your treatment plan, taking your prescribed medications and attending regular therapy appointments.
You can find practical and life-changing treatments for GAD and other anxiety disorders at Gateway Foundation. We offer special remedies such as direct therapist referral, input from anxiety and depression treatment specialists and forms of psychotherapy like cognitive behavioral therapy to help you reframe the way you perceive and cope with daily life events and stressors.
Gateway’s therapies help our patients overcome their addiction and address any co-occurring mental health conditions head-on. Our anxiety treatment programs provide a full range of holistic treatment plans individualized for your situation to help you begin and continue your journey to recovery. Developing and honing the skills you learn in psychotherapy can help you facilitate success after treatment and practice lifelong coping skills.
Find Help for Your Anxiety Today With Gateway
Receiving help for GAD can help you take back control of your life, and proper treatment will provide you with increased relief and safety. Gateway Foundation provides reliable, evidence-based treatment options for mental health and substance use. With over 50 years of experience in the Illinois area, Gateway can provide a continuum of high-quality care through our compassionate, non-judgmental staff.
Gateway offers inpatient and outpatient services to relieve anxiety symptoms and address substance use medically and professionally. Contact us today for trusted treatment for substance use disorders and help with GAD.



